The future of automated manufacturing (and why humans still matter)
Automation in manufacturing has been evolving for decades, but its true impact isn’t in replacing people, it’s about making them more capable. We spoke with Mika Anttila, one of Visual Components’ founders, to explore how automation is reshaping factory jobs, the skills needed for the future, and what lies ahead for smart manufacturing.
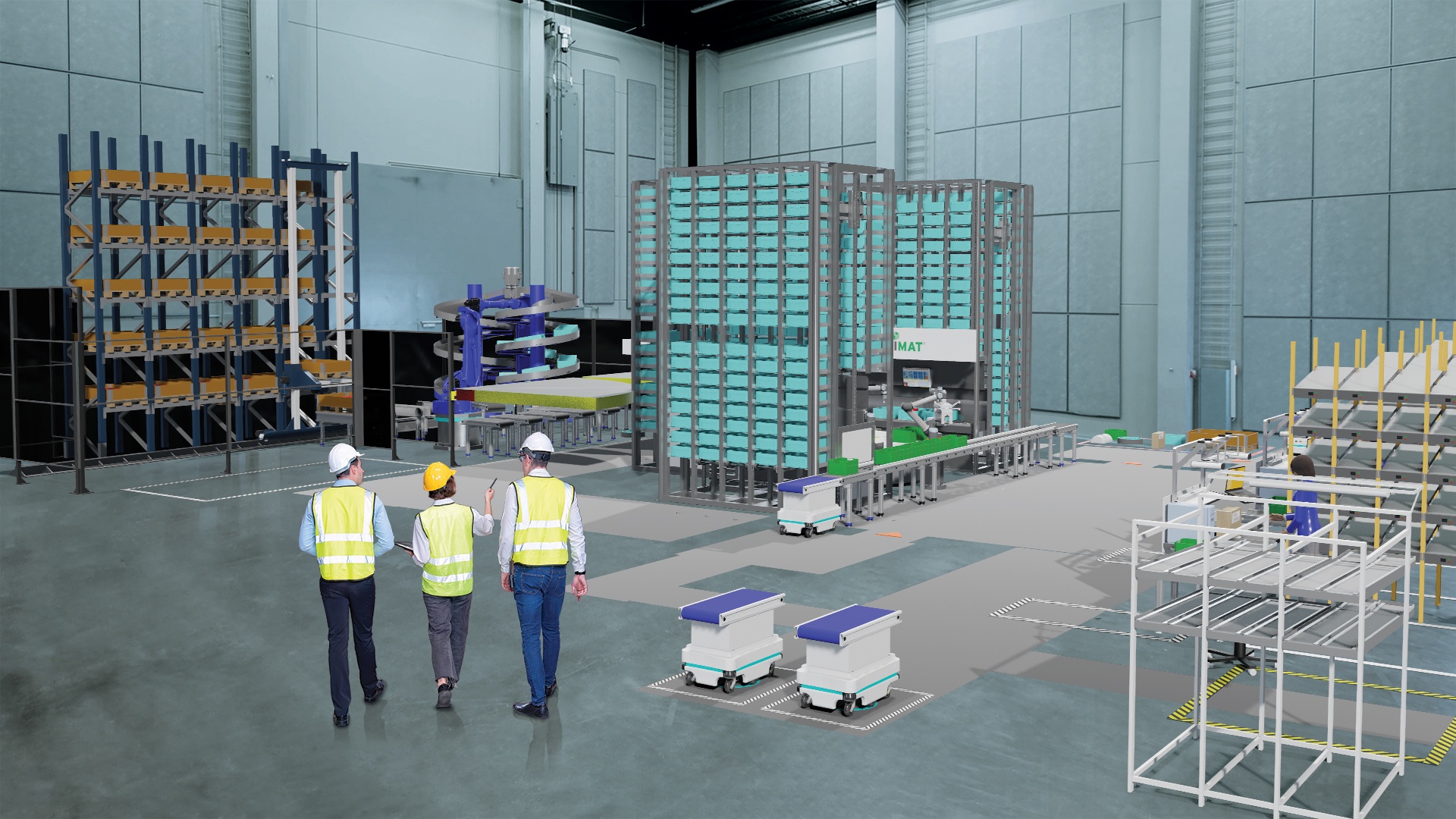

The future of automated manufacturing (and why humans still matter)
Automation in manufacturing is no longer a novel concept. Robots and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) have been on factory floors since the 1960s. Every decade since has seen new technologies making production less reliant on manual labor. But the key takeaway isn’t that automation will eventually make humans obsolete: instead, automation is more about making us more capable.
How automation has reshaped jobs in manufacturing
To explore this topic further, we spoke with Mika Anttila, one of our founders at Visual Components. He shared his perspective on where automation is heading and how human roles in manufacturing are evolving.
“Automation isn’t necessarily just about efficiency anymore. The key is flexibility — how we enable workers to handle new challenges rather than pushing the workers aside.”
Factory jobs today are almost unrecognizable compared to what they were 30 years ago. Back then, manufacturing was dominated by manual labor and a focus on physically assembling products. Individual operators were typically assigned to a single part of the assembly process, as well as running machines to keep things moving.
The introduction of robots and PLCs in automotive factories transformed production, but it didn’t eliminate human roles. Instead, it created new ones with a focus on flexible automation, something that is increasingly apparent today.
“If you look at the automotive industry, for example, we started with robotic arms doing fixed, repetitive tasks,” Mika shared. “Now, we have mobile and collaborative robots that adjust their actions in real-time and work alongside people.”
Sensors, machine learning, and digital platforms enable machines to optimize processes independently, creating a new need for workers to manage and enhance these systems.
The transition to smarter, more flexible automation
Automation is no longer rigid and predefined. The shift to flexible, intelligent automation allows manufacturers to adapt to changing market needs. Traditional production lines were built for mass production, where everything was standardized. But today’s consumers expect personalized products, which means factories require adaptable solutions.
Mika stresses that the key to future automation is adaptability.
“In the past, automated systems followed rigid sequences,” he said. “Now, we’re seeing automation that dynamically responds to changing production needs, with AI and robotics working alongside people instead of replacing them.”
But how will the manufacturers and those working in the factories of today adapt to these changes?
New opportunities and skills required in future factories
As technology advances, new career opportunities are emerging, particularly in roles that bridge human and machine collaboration.
A 2023 workforce study we conducted found that 87% of companies now prioritize upskilling their employees to keep pace with an increasing shortage of workers, such as welders, and automation more broadly.
Mika believes manufacturing workers will shift toward higher-level problem-solving.
“We’re moving toward a scenario where workers are not just operators, but they’re the supervisors of automation, as well as the people who make critical decisions and fine-tune any processes as needed,” he said.
Some of these roles could include Automation Engineers, Digital Twin Experts, Virtual Commissioning Engineers, Robot Programmers, and similar positions. These roles emphasize digital literacy, problem-solving skills, and adaptability.
How simulation is helping drive the next phase of automation
Simulation is a powerful tool in modern automation, enabling manufacturers to conduct virtual commissioning—testing, refining, and optimizing production processes—before real-world deployment.
Mika underscores the growing role of simulations in bridging planning and execution.
“The ability to validate entire production workflows before they go live is going to be increasingly possible,” he shared. “This means fewer errors, better resource allocation, and a much faster response to changes.”
Major benefits of simulation include:
- Lower risk as manufacturers can test new automation systems digitally before implementation.
- Smarter training with workers being able to see how a manufacturing process will work in a simulated environment.
- Human-robot collaboration is a bit better to plan for, ensuring workflows are designed for efficiency and safety.
- Improved quality of automation engineering by allowing comprehensive tests of automation applications, which can dramatically enhance the overall quality.
- Cost reduction by minimizing trial and error in physical setups.
- Rapid adjustments to system designs, enhancing flexibility in automation processes.
- Early identification of potential design flaws or performance issues.
What will factories look like in 2045?
Fast forward 20 years, and factory floors will be almost unrecognizable. AI-driven robotics, real-time digital twins, and generative design will make us rethink how we plan and operate factories. Instead of manually operating machines, workers will shift into roles as system orchestrators—overseeing intelligent automation and ensuring everything runs smoothly.
Mika predicts that AI-driven automation will become more intuitive than ever. “Machines won’t need to be extensively programmed anymore,” he explains. “Instead, they’ll learn by observing real-world processes, adapting to new tasks the way humans do.”
This kind of flexibility will extend to production layouts as well. AI-generated layouts will automatically adjust to shifting demands, keeping workflows optimized no matter how the market evolves.
Augmented reality (AR) will also help reshape how operators interact with their environments. With AR interfaces, workers will be able to engage with virtual factory models in real time, gaining deeper insights and making more informed decisions.
Humanoid robots will also undoubtedly become a regular part of the manufacturing workforce. These robots will work alongside human teams, handling complex, high-precision tasks that once required skilled human hands.
One thing is certain: the factories of 2045 will be smarter, more adaptable, and more efficient than ever before.
Building a future where automation and humans thrive together
The future of factory work isn’t about making humans obsolete — it’s about enhancing human capabilities. As automation takes on the heavy lifting, human workers will play a bigger role in guiding, fine-tuning, and improving these smart systems. The real challenge? Making sure people have the right skills and tools to thrive in this new era.
At Visual Components, we believe the best factories are built on teamwork—between people, machines, and technology. With our simulation and robot offline programming (OLP) tools, we help companies and their workers step confidently into the future of manufacturing.
About Visual Components
Founded by a team of simulation experts and amassing over 20 years in business, Visual Components is one of the pioneers of the 3D manufacturing simulation industry. The organization is a trusted technology partner to a number of leading brands, offering machine builders, system integrators and manufacturers a simple, quick and cost-effective solution to design and simulate production processes and offline robot programming (OLP) technology for fast, accurate and error-free programming of industrial robots.
Want to learn more about the benefits of our solutions for your business? Contact us today!
Further reading
Robot programming for industrial processes with Visual Components OLP software
Robot programming is advancing with offline programming, enabling manufacturers to optimize robotic tasks virtually without disrupting production. This minimizes downtime, improves accuracy and streamlines processes like welding, spraying, processing and...
How robot offline programming drives efficiency in high-mix, low-volume production lines
Frequent changeovers and small batch sizes can slow down production, but they don’t have to. With robot offline programming (OLP), manufacturers in high-mix, low-volume production can program robots 10 times...

Smarter warehouse planning starts with simulation
How can businesses design warehouses that operate efficiently from day one while keeping labor costs and other expenses in check? The key is smart planning and validation with simulation tools...