Robot programming for industrial processes with Visual Components OLP software
Robot programming is advancing with offline programming, enabling manufacturers to optimize robotic tasks virtually without disrupting production. This minimizes downtime, improves accuracy and streamlines processes like welding, spraying, processing and assembly. Upskilling workers in robot programming ensures they can fully leverage automation for sustained manufacturing success.
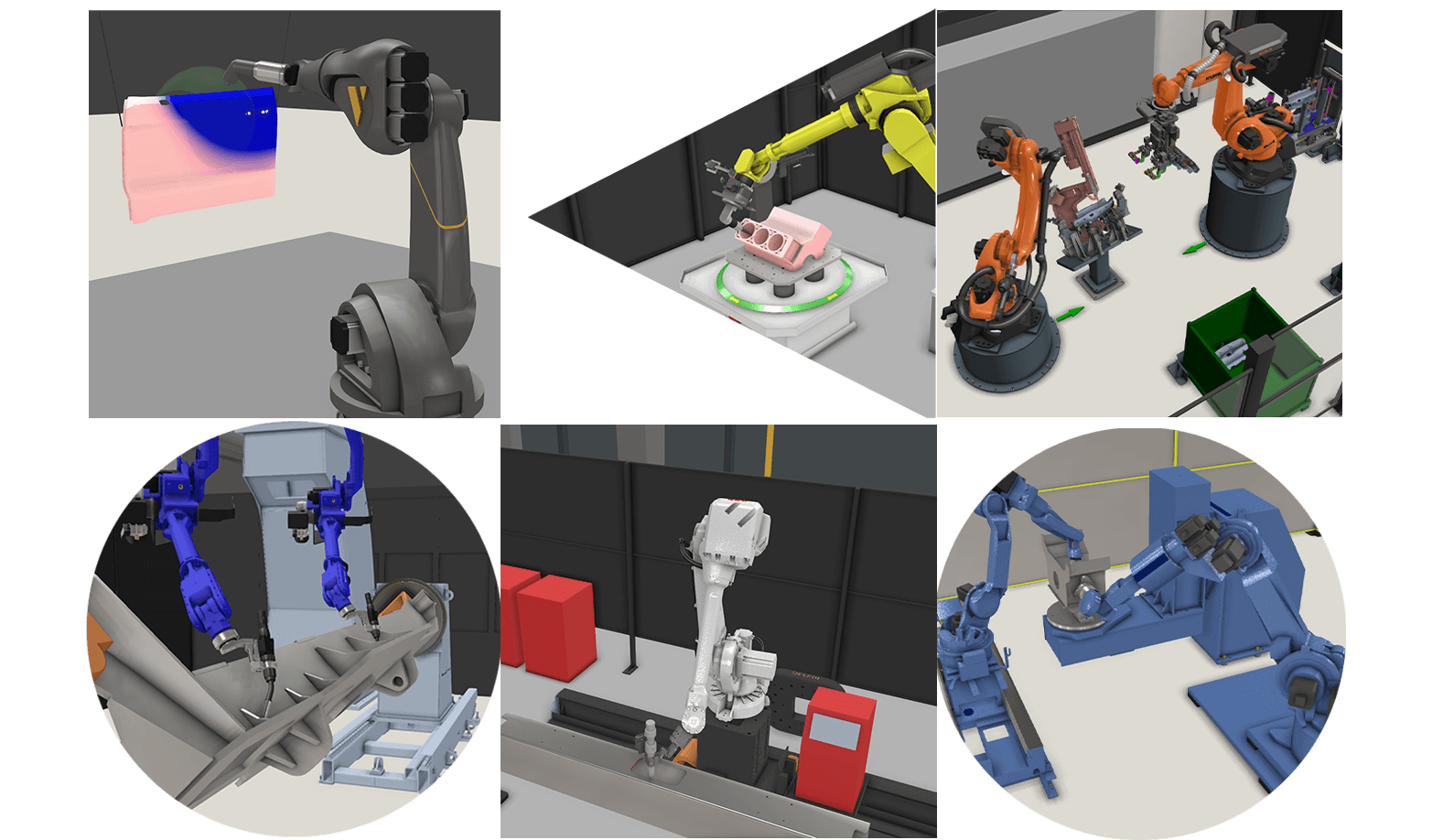
Industrial robots are essential for manufacturing efficiency, but manual robot programming can be time-consuming and complex. For processes like welding, spraying, material processing and assembly, manual robot programming introduces challenges in accuracy, repeatability and downtime. This is where robot offline programming (OLP) makes a difference.
Instead of manually teaching the robot point by point with a teach pendant, OLP allows manufacturers to program robots in a virtual environment before deploying them to the shop floor. This reduces programming time, minimizes production interruptions and ensures high-quality results. Let’s explore why manual programming is difficult for various industrial robotic processes—and how OLP solves these challenges.
Robot programming for welding: Achieving accuracy and efficiency
Welding applications present challenges in access, orientation and path accuracy—areas where robot offline programming (OLP) provides precise control and repeatability. Complex welds often require numerous accurate points, making manual programming time-consuming and prone to inconsistencies. Teaching a robot to follow a 3D arc while maintaining the correct torch angle and distance can result in errors. These inaccuracies lead to rework, quality issues and extended downtime, as the robot cell remains out of production until programming is complete.
With OLP, welding programs are created in a virtual environment using CAD models of the robot cell. Users can define precise torch paths, simulate movements and check for potential collisions before deployment.
Additionally, Visual Components OLP software enables the direct import of welds from model-based definition (MBD), eliminating the need for manual weld creation. Instead of creating each weld path individually, MBD automates the transfer of critical welding parameters, ensuring accurate placement and consistency across parts. This automation reduces programming time, minimizes errors and accelerates production throughput.
Once verified, the program is transferred to the robot and production resumes immediately—eliminating costly delays and ensuring consistent, high-quality welds.
Robot programming for spraying: Optimizing coverage and performance
Just like in welding, orientation is critical in spray applications such as painting and coating. Achieving consistent coverage requires precise control over speed, angle and standoff distance. Manual robot programming makes this difficult, often leading to overspray, uneven coating and excessive material waste. Fine-tuning spray paths manually is time-consuming and every adjustment increases production downtime. Additionally, testing spray patterns directly on the production line drives up costs due to wasted materials and increased cycle times.
With robot offline programming, manufacturers can define and simulate optimized spray paths in a virtual environment. This ensures even coverage, eliminates overspray and minimizes material waste—all without interrupting production. By perfecting spray applications offline, manufacturers cut down setup time, minimize production interruptions and achieve consistent, high-quality finishes while keeping costs under control.
Robot programming for processing: Ensuring accuracy and consistency
Processing tasks like bead blasting and deburring require complex, highly accurate tool paths. Even slight deviations in pressure, speed or positioning can result in defective parts. Manually programming these intricate paths is not only time-consuming but also difficult to replicate consistently across multiple parts. Each adjustment requires stopping production, leading to costly downtime and reduced throughput.
Robot offline programming streamlines this process by enabling manufacturers to create and optimize cutting paths with CAD-based accuracy. The software fine-tunes tool angles, pressures and movements to ensure repeatable, high-quality results across every part. By programming offline, manufacturers avoid production disruptions, reduce material waste and accelerate setup time—leading to higher throughput and lower operational costs.
Robot programming for assembly: Optimizing precision and production throughput
Robotic assembly processes involve complex synchronized movements, precise part placement and seamless coordination with other automated systems. Manually programming these tasks requires extensive trial and error, increasing setup time and production delays. Even small positioning errors can lead to defective products and inefficiencies on the production line.
With OLP, manufacturers can define and simulate assembly sequences in a virtual environment,, eliminating the guesswork of manual programming. This enables accurate component placement, smooth workflow coordination and faster changeovers between product variations. OLP also provides advanced control over gripper orientation for grasping and insertion tasks, enabling reliable, repeatable operations without extensive manual adjustments.
To further enhance accuracy, OLP integrates gravitational tables, laser sensors and cameras to validate positioning during program execution. These technologies detect discrepancies between CAD-defined positions and real-world part locations, allowing the system to adjust offsets dynamically. This ensures consistent alignment, minimizes defects and maximizes assembly line productivity.
Why workforce upskilling in robot programming matters
As industries accelerate their adoption of robotics, the demand for skilled robot programmers continues to outpace supply. Upskilling workers in robot programming is essential for bridging the skills gap, accelerating automation deployment and maximizing the return on robotics investments. By equipping operators and engineers with robot offline programming expertise, companies can streamline production, reduce costly downtime and empower their teams to confidently manage and optimize robotic systems.
Visual Components OLP software provides a simulation-driven learning environment, allowing users to develop programming skills, test and refine robotic movements and troubleshoot potential issues—without interrupting production. This hands-on approach helps teams master multi-robot coordination, optimize complex workflows and drive continuous process improvements. Investing in workforce development not only reduces reliance on external programming resources but also strengthens a company’s ability to adapt to future automation challenges with in-house expertise.
The future of robot programming: smarter, faster and scalable
As industrial automation advances, manufacturers must adopt intelligent solutions that reduce robot programming time, enhance accuracy and keep production lines running at full capacity. Robot offline programming eliminates the bottlenecks of manual teaching, reducing rework, minimizing downtime and ensuring optimal path accuracy. Whether for welding, spraying, assembly or processing, OLP enables robots to be programmed rapidly, consistently and with minimal disruption—driving higher productivity and long-term operational efficiency.
If you’re struggling with manual robot programming challenges, it’s time to explore how robot offline programming can streamline your manufacturing process. Contact us to learn more about implementing OLP in your production workflow.
Further reading

The future of automated manufacturing (and why humans still matter)
Automation in manufacturing has been evolving for decades, but its true impact isn’t in replacing people, it’s about making them more capable. We spoke with Mika Anttila, one of Visual...
How robot offline programming drives efficiency in high-mix, low-volume production lines
Frequent changeovers and small batch sizes can slow down production, but they don’t have to. With robot offline programming (OLP), manufacturers in high-mix, low-volume production can program robots 10 times...

Smarter warehouse planning starts with simulation
How can businesses design warehouses that operate efficiently from day one while keeping labor costs and other expenses in check? The key is smart planning and validation with simulation tools...